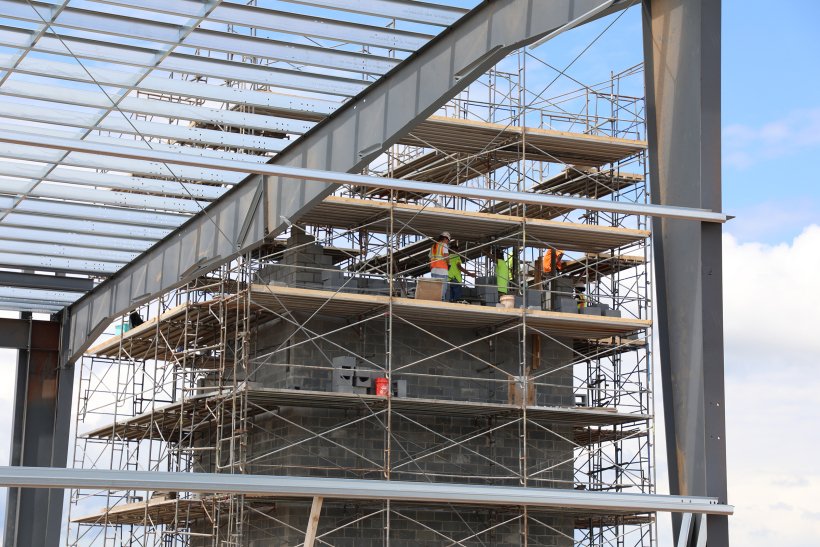
Construction crews work to erect the platform’s structural framework. (Photo: DOE)
Crews are making significant progress on the construction of the K-25 viewing platform at the Oak Ridge Reservation in Tennessee, the Department of Energy’s Office of Environmental Management announced on August 20. When completed next year, the elevated platform will offer a sweeping panoramic view of the massive 44-acre footprint of the K-25 Building, which once produced enriched uranium used in the weaponry that ended World War II.
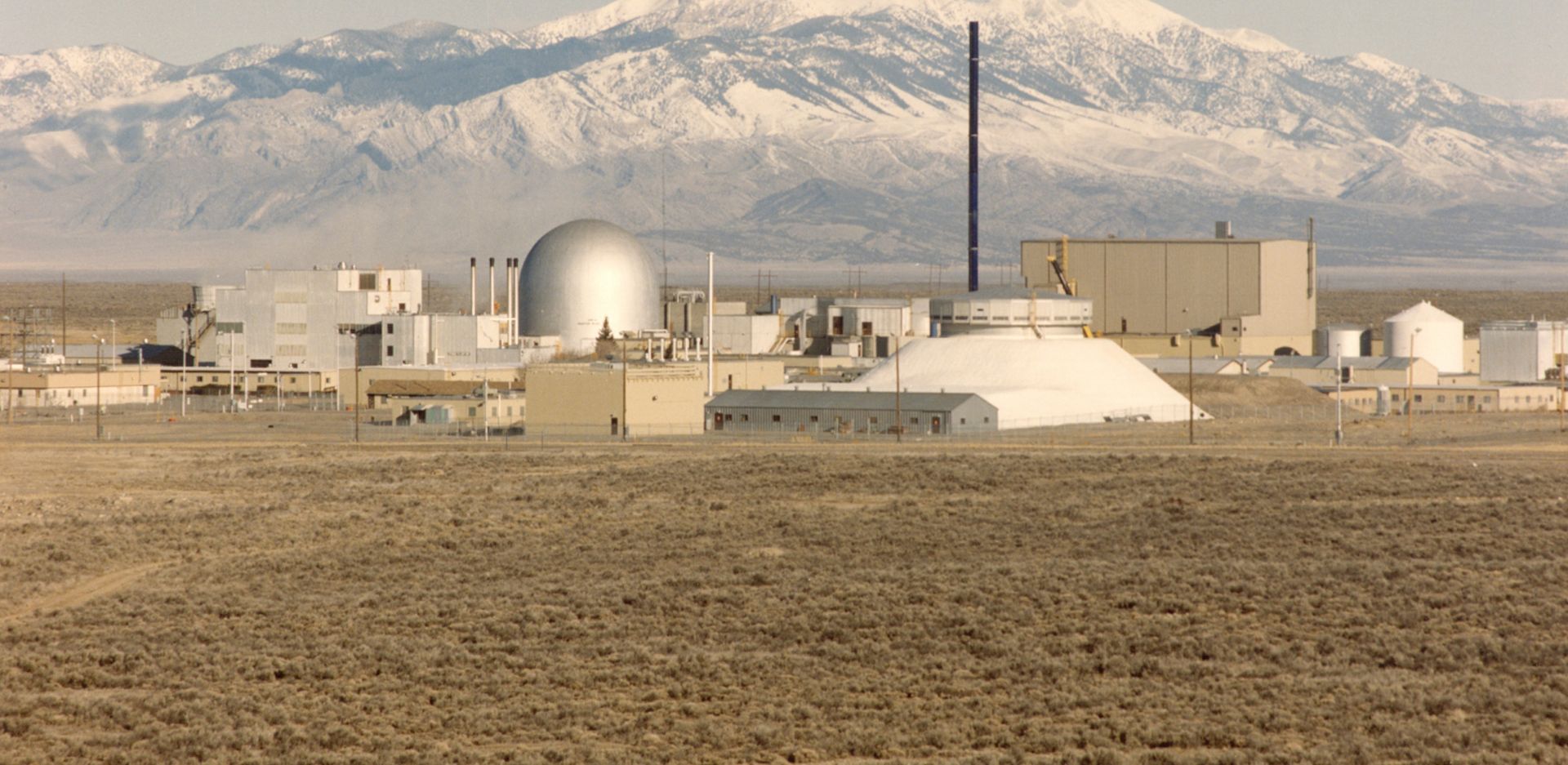
The Argonne-West laboratory site before it was merged with the Idaho National Engineering and Environmental Laboratory into today’s Idaho National Laboratory. The silver dome in the photo is Experimental Breeder Reactor-II, the silver structure with the flat top and sloping sides is the Zero Power Plutonium Reactor, and the brown boxlike structure behind ZPPR is the Hot Fuel Examination Facility. (Photo: Argonne National Laboratory)
Idaho’s nuclear energy history is deep and rich. The National Reactor Testing Station (NRTS) began its history as an artillery testing range in the 1940s.1 Following World War II, Walter Zinn, Argonne National Laboratory’s founding director and Manhattan Project Chicago Pile-1 project manager, proposed to the Atomic Energy Commission that a remote location be found for building test reactors. In 1949, he and Roger S. Warner, AEC’s director of engineering,2 developed a list of potential sites from which the NRTS was selected. Over the decades, quite a few companies and AEC national laboratories built 52 experimental and test reactors at the NRTS, including 14 by Argonne.3 (For a brief AEC video on the NRTS, see youtube.com/watch?v=C458NsH08TI.)
The exterior of the Clementine nuclear reactor at Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory. (Photo: LANL)
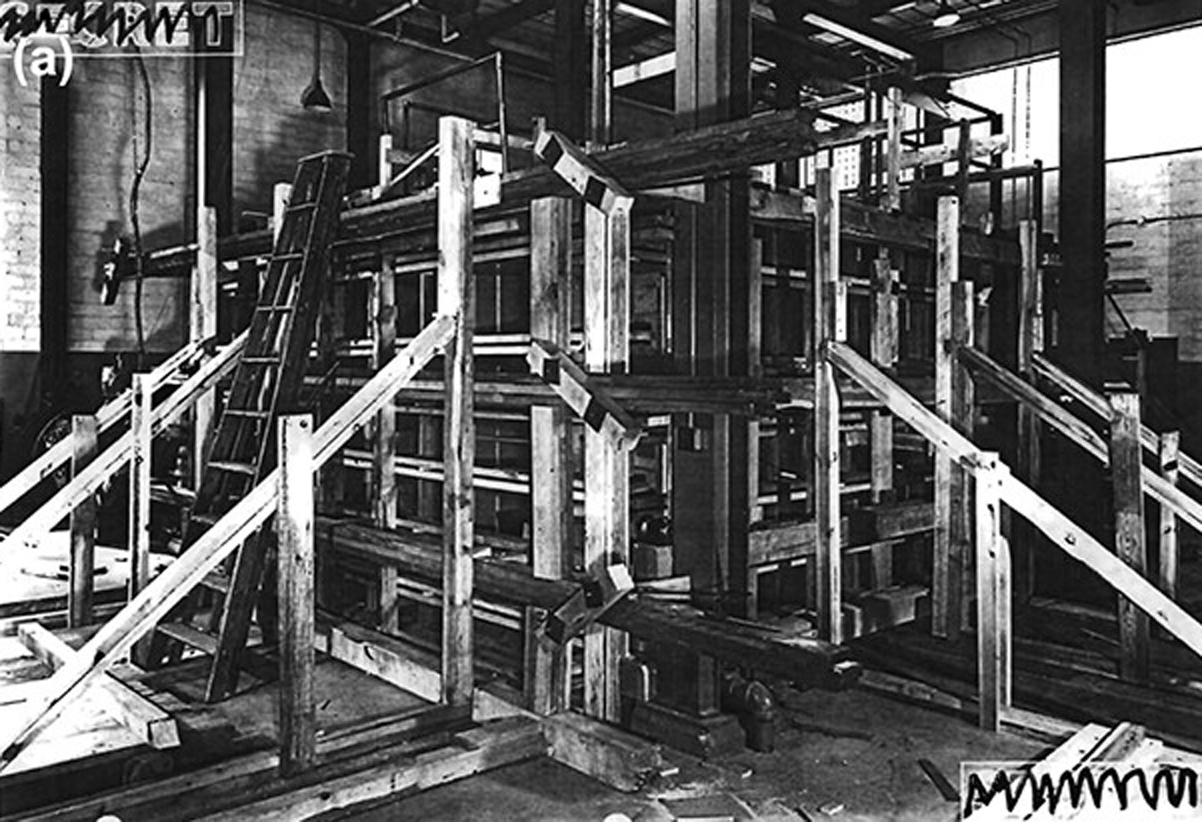
In March 1949—75 years ago this month—the 25-kilowatt reactor known as Clementine reached full power. As an experimental reactor, it had a rather long and successful run. It was the world’s first fast neutron (high-energy) reactor and operated from initial criticality in 1946 to final shutdown in 1952.
Radioisotopes target cancer, improve imaging, and have myriad other medical uses
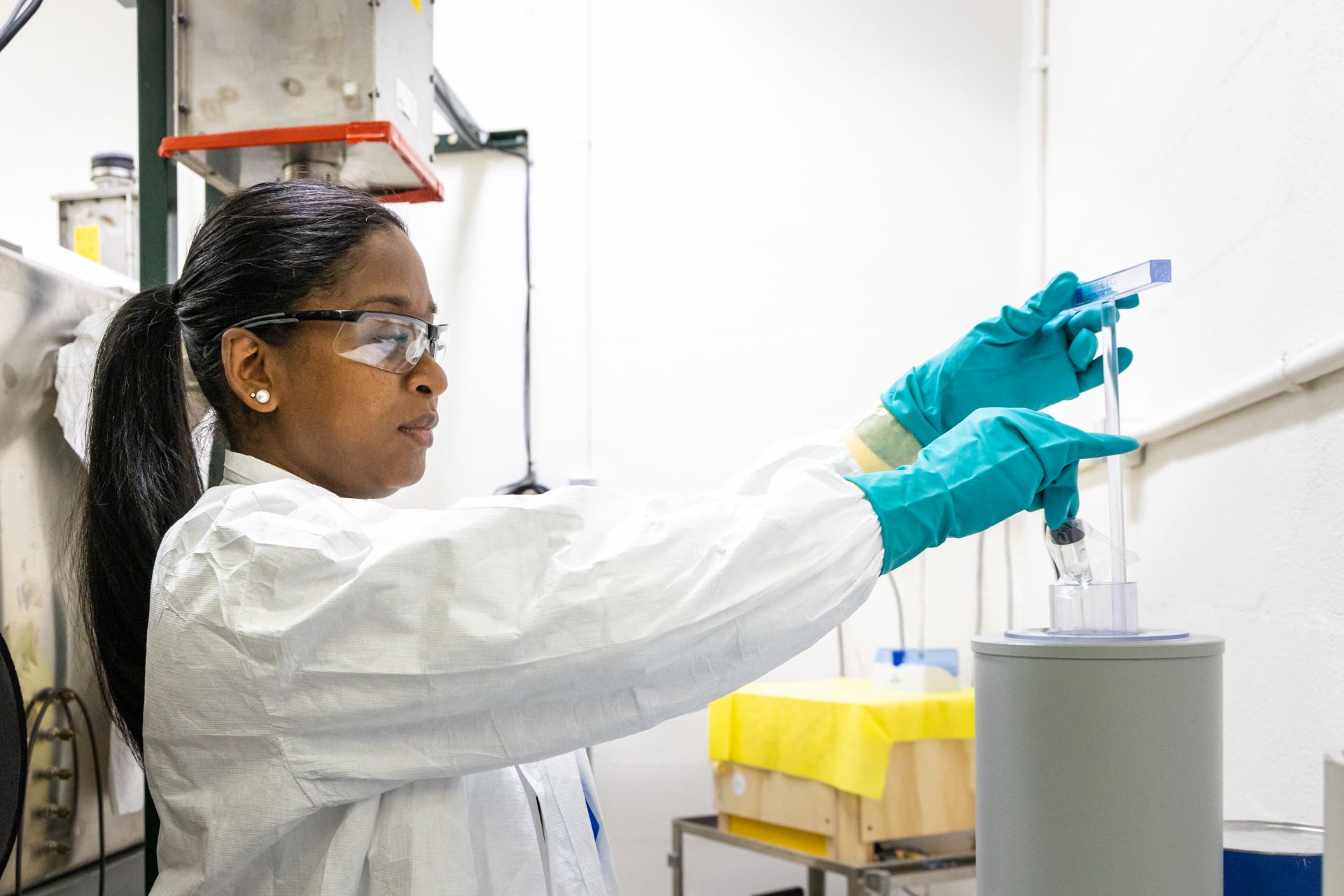
ORNL radioisotope manufacturing coordinator Jillene Sennon-Greene places a shipment vial of actinium-225 inside the dose calibrator to confirm its activity is within customer specifications. (Photo: Carlos Jones/ORNL, DOE)
On August 2, 1946, 1 millicurie of the isotope carbon-14 left Oak Ridge National Laboratory, bound for the Barnard Free Skin and Cancer Hospital in St. Louis, Mo.
That tiny amount of the radioisotope was purchased by the hospital for use in cancer studies. And it heralded a new peacetime mission for ORNL, built just a few years earlier for the production of plutonium from uranium for the Manhattan Project.
Front face of the B Reactor at the Hanford Site. (Photo: DOE)
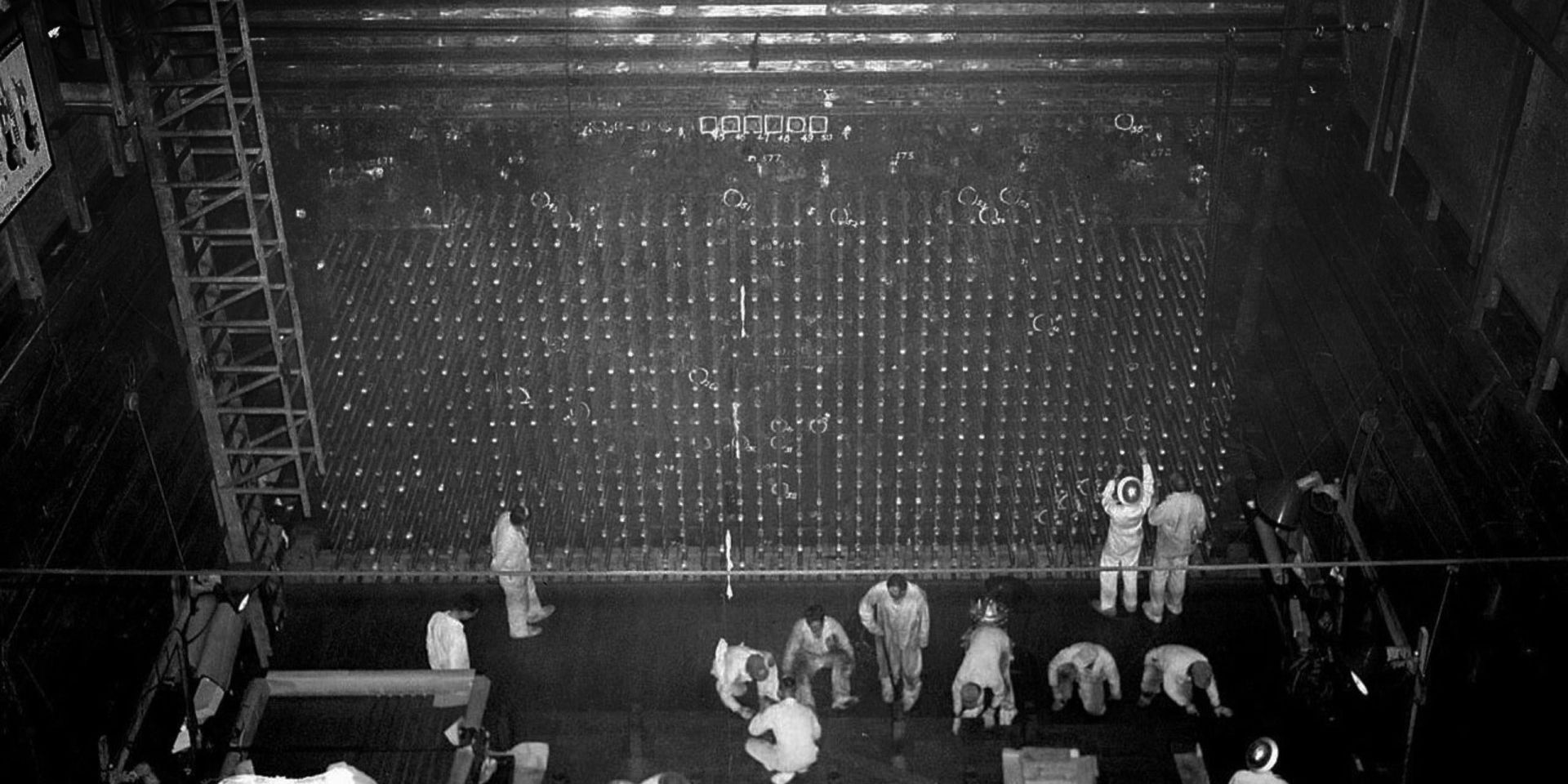
In remote southeastern Washington you will find the sprawling Hanford Site, which was constructed to produce plutonium for the Manhattan Project. Within this complex is the first plutonium production reactor, the Hanford B Reactor. The DuPont Corporation was responsible for construction and operation of the B Reactor. Due to the urgency of the Manhattan Project, construction was completed in just over a year, and The B Reactor went critical on September 26, 1944. After the needs of the Manhattan Project were satisfied, the reactor was briefly shut down and then restarted to produce plutonium for roughly another 20 years, supporting Cold War efforts. In addition to plutonium production, the B Reactor also pioneered the process to produce tritium for the first-ever thermonuclear test.
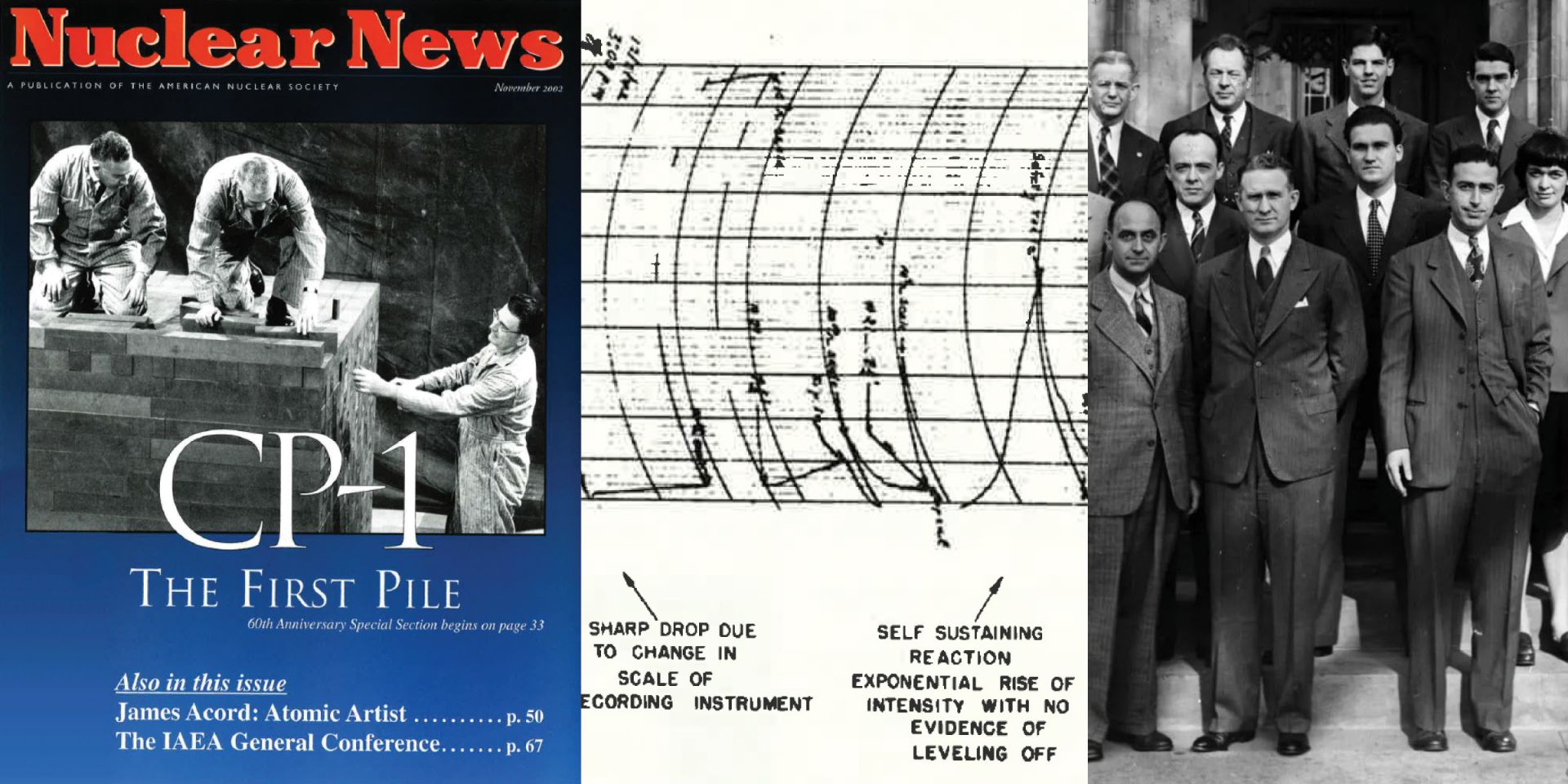
A replica of the chianti bottle signed by many of those present on December 2, 1942, alongside the image of a document signed 20 years later by most of those present (Photo: ANL); a portion of a photo of CP-1 scientists taken on December 2, 1946 (Photo: ANL); January 1993 Nuclear News coverage of CP-1 50th anniversary commemorations during the 1992 ANS Winter Meeting.
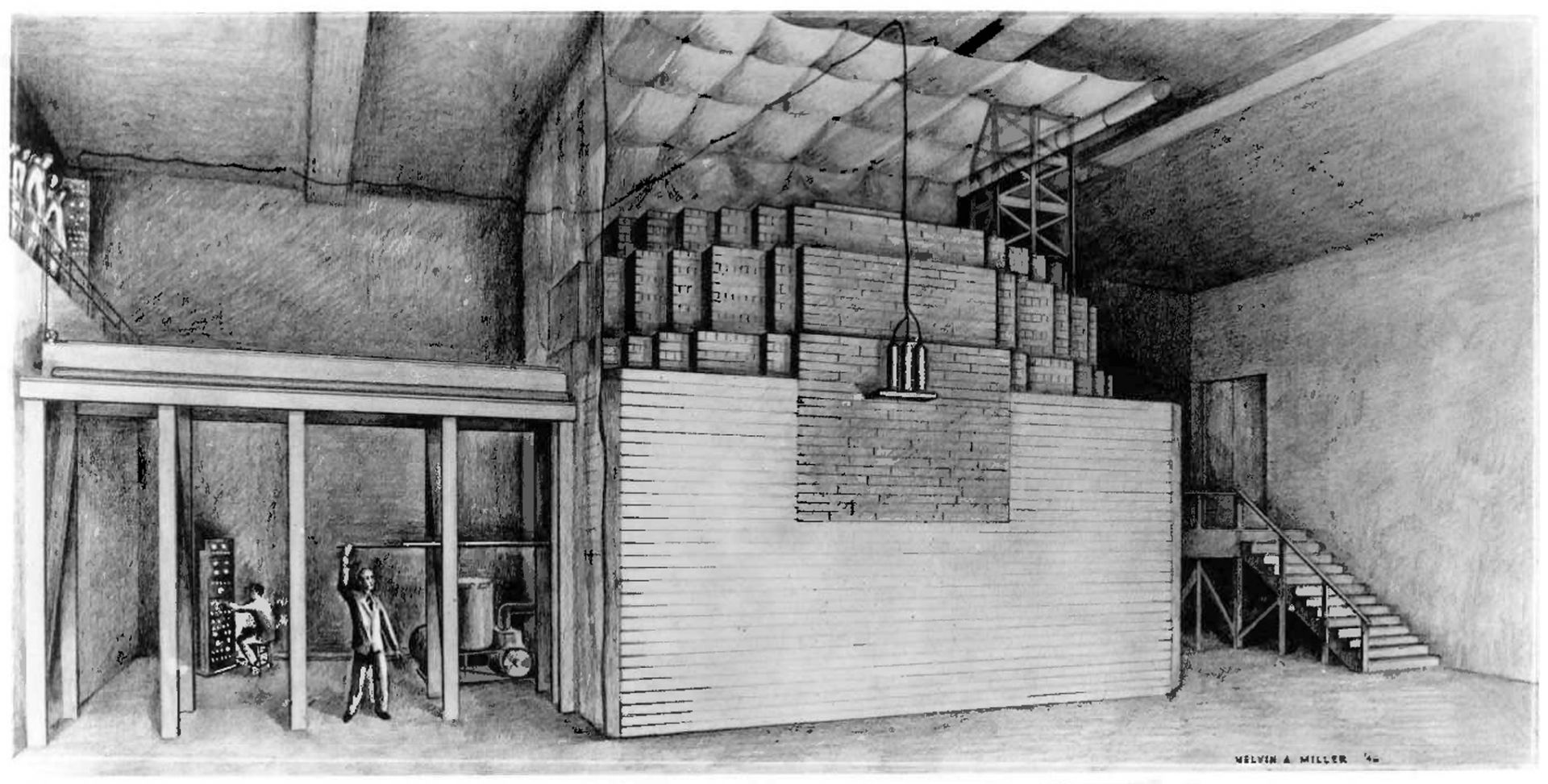
Nuclear Newswire is back with the final #ThrowbackThursday post honoring the 80th anniversary of Chicago Pile-1 with offerings from past issues of Nuclear News. On November 17, we took a look at the lead-up to the first controlled nuclear chain reaction and on December 1, the events of December 2, 1942, the day a self-sustaining nuclear fission reaction was created and controlled inside a pile of graphite and uranium assembled on a squash court at the University of Chicago’s Stagg Field.
On December 2, 1942, a group of 49 scientists led by Enrico Fermi created the world’s first controlled, self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction underneath the University of Chicago’s Stagg Field football stadium. Some of those present went on to found Argonne National Laboratory. (Image: Argonne)
At a moment of global crisis, in a windowless squash court below the football stadium bleachers at the University of Chicago, a group of scientists changed the world forever.
On December 2, 1942, a team of researchers led by Enrico Fermi, an Italian refugee, successfully achieved the world’s first human-created, self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction. Racing to beat Nazi Germany to the creation of an atomic weapon, the team of researchers, working as part of the Manhattan Project, split uranium atoms contained within a large graphite pile—Chicago Pile-1, the first nuclear reactor ever built.
From left, the cover of the December 1962 issue of NN, featuring a model and a medal, both displayed at the 1962 ANS Winter Meeting; a photo of CP-1 during construction, as published in the November 1992 issue of NN; the opening page of a chronological account of CP-1, published in November 1992 to mark the 50th anniversary.
As we approach the 80th anniversary of controlled nuclear fission, Nuclear Newswire is prepared to deliver not one but three #ThrowbackThursday posts of CP-1 highlights unearthed from past issues of Nuclear News.
ANS was founded in 1954, nearly 12 years after the first controlled nuclear chain reaction was achieved on December 2, 1942, inside a pile of graphite and uranium assembled on a squash court at the University of Chicago’s Stagg Field. By 1962, ANS was prepared to “salute the 20th anniversary of the first chain reaction” at their Winter Meeting, displaying a model of Chicago Pile-1 and presenting a specially cast medal to Walter Zinn, a representative of Enrico Fermi’s scientific team. Over the years, ANS has continued to mark significant anniversaries of CP-1 at national meetings and in NN.
Ultra Safe Nuclear staff in front of the new pilot fuel fabrication facility in Oak Ridge, Tenn. (Photo: USNC)
Ultra Safe Nuclear Corporation (USNC), an advanced reactor and reactor fuel developer, announced last week that it plans to begin operations this summer at its Pilot Fuel Manufacturing (PFM) facility in Oak Ridge, Tenn., pending the receipt of the requisite state and local permits. The facility is located in the East Tennessee Technology Park, site of the Manhattan Project’s K-25 gaseous diffusion plant. USNC purchased an 8.7-acre site—which included a preexisting industrial building—from Heritage Center LLC in 2021.